Alas, we’re not living in an ideal world where everyone respects other people’s right to private property and privacy. We’re talking about hackers now — cybercriminals who’re constantly looking to exploit weak security spots in websites to steal data or pull off their dirty tricks.
According to a report published last year, the majority of hackers’ targets (nearly 60%) were small businesses. That’s because small and mid-sized enterprises can’t afford to spend as much on protecting their websites from hackers as big companies can.
It’s not so hopeless, though. If you’re a small business owner, you can effectively prevent cyber crooks from shamelessly breaking into your website without having to spend a fortune. Just follow our guide below.
HOW HACKERS CAN USE YOUR SITE TO THEIR BENEFIT
Even a site comprised of just a bunch of static HTML files with plain text and a few images can attract the attention of cybercriminals. What can they use it for?
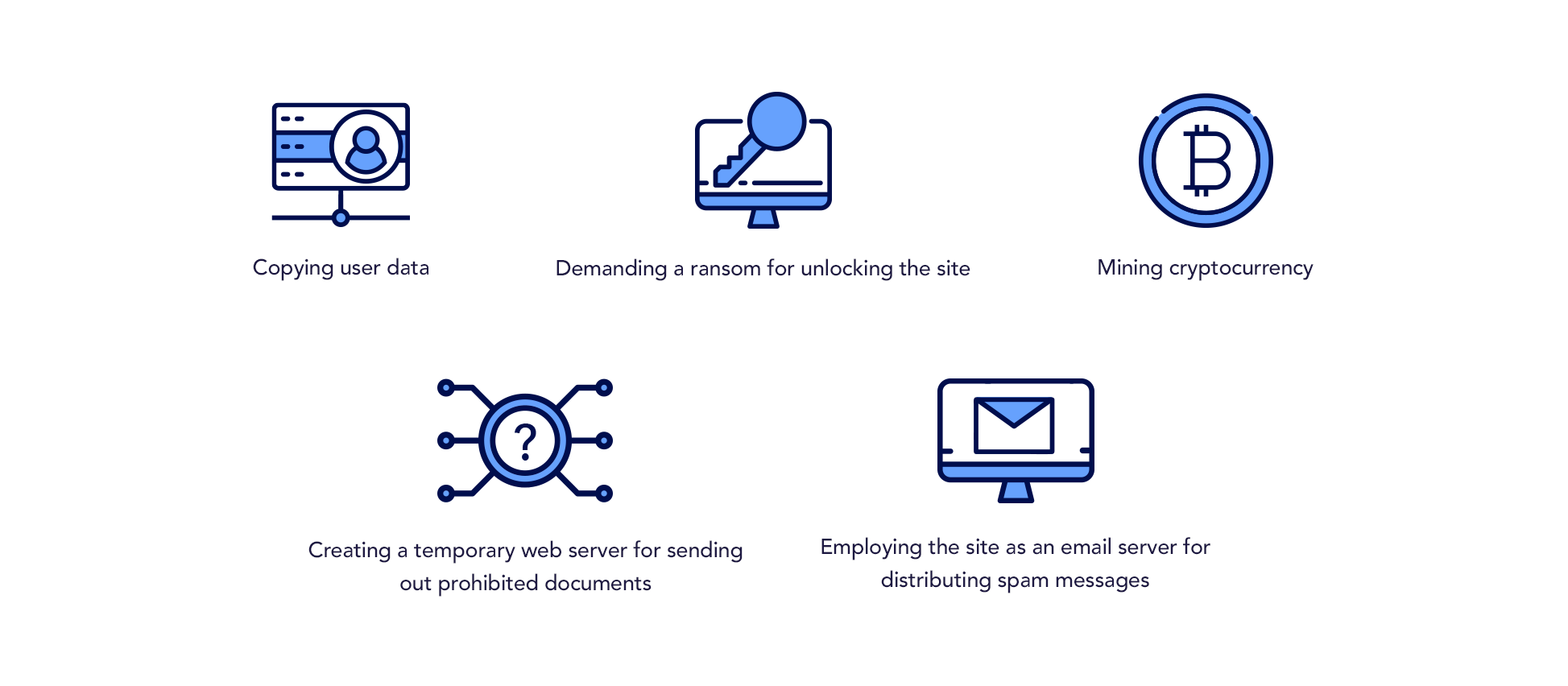
This is by no means a full list of hackers’ “ingenious” ideas. It keeps growing as new technologies come into existence. When can you say that there are other, unwanted administrators of your site?
SOME TELLTALE SIGNS THAT YOU’VE FALLEN VICTIM TO A HACKER

1. You have far fewer visitors to your site than before
After breaking into your website, hackers implant their code into your pages or change your code for theirs entirely. This enables them to redirect visitors to other locations.
Once search engines discover that your site is out of order and acting suspiciously, they push it down SEO rankings. This further reduces the number of visitors, who can’t find your site as easily as before.
Normally, in this case, plugins and themes are the soft spots that hackers can exploit automatically.
Signed-in users don’t see the ads. Only visitors who’ve come to your website by clicking a link on a search results page or on another site do. As a result, hackers can be the masters on your site for ages until you finally discover their presence.
3. You can’t sign in
If you can’t access your dashboard by entering the login/password pair you’ve typed in dozens of times before, it means you’re in trouble. The most likely cause of this problem is that your login is too simple and predictable like ‘root,’ ‘admin,’ or ‘test.’ That makes your site an easy target for hackers.
4. The content of your main page has been altered without you being aware of it
Often, cybercriminals show off their coding skills or try to make a fool of you by messing up with your content and adding their own “funny stuff” for good measure. In other cases, the damage can be far more severe, with hackers letting you know they want money from you by placing a message right on the main page.
We anticipate your next question, “How can I keep hackers away?” The answer is, “You can do a lot.” Read on.
KEY ANTI-HACKER GUIDELINES

1. Find a High-Quality Hosting Provider
Be careful when choosing a hosting provider. While it’s tempting to save a few dollars, you may bitterly regret your decision afterward. A cheap server divided among a large number of sites can be the perfect breeding ground for viruses that will spread from one site to another.
Take your time and perform a thorough search for a reliable hosting company with a good renommé and reasonable pricing plans. Avoid twopenny-halfpenny hosting providers who don’t care about the security of their servers and don’t perform regular scans for malware and malicious code
2. Coin a Unique Login. Make Your Password Impossible to Guess
Hackers adore simple logins and short, easy-to-crack passwords.
First off, if your administrator login is still ‘admin,’ change it immediately. Your new login should not be related to your life or work. For example, choosing your pet’s name or the name of your favorite football team as your login or its part is not advisable. A hacker can find it out just by visiting your Facebook page, for example.
What makes a good password? Read Google’s recommendations to find it out. In addition, make sure you don’t have a single user with a weak password.
Storing passwords securely is also extremely important. We highly recommend encrypting all your sensitive data, including passwords, by using a one-direction algorithm (SHA or equivalent).
This article describes various methods to hide real values of passwords.
Other preventive measures as far as passwords are concerned:
- Allowing users to type in the login/password pair only a few times in a row and blocking them if they fail to enter the right credentials. This can be done by means of various extensions such as this.
- Choosing a new password on a regular basis (every seven or fourteen days).
3. Use Secure Socket Layer Encryption Protocol

The old faithful http protocol is still actively used by many websites, but sending data in this way is like sending an open box of candy by mail. Everyone can take as many as they like along the way.
The Secure Socket Layer protocol is a completely different matter. It enciphers every single bit thrown over the wires in a bullet-proof fashion. Thus, hackers have no hope of breaking the encoding wrapper and seeing what information that bit carries. In highly sensitive environments, organizations often combine SSL with data diode solutions to guarantee one-way traffic flow and protect critical systems from external threats.
Most SSL certificates cost money, although many hosting providers may include them free in your plan. The paid option offers deeper validation than the free one. For the differences between free and paid SSL certificates, read this post.
4. Keep Your Software Up to Date and Remove Plugins You No Longer Use
Hackers are constantly monitoring the web for security holes. Once they find a vulnerability, they share this information with their “brothers,” and attacks begin all over the place.
Vendors are usually quick to react to security alerts and make patches to eliminate threats. You can learn about those improvements from an RSS feed, a mailing list, or corresponding notifications when you log into the dashboard.
So, we recommend checking for updates often, preferably every day. When you leave an old version of a plugin or theme around, you are running the risk of being hacked. A poignant example is the recent wave of hacker attacks on WordPress and Magento sites through an outdated version of the Adminer database management tool. You can read about this exploit on our blog.
Also, review all your plugins and delete those you no longer need, even if you’ve disabled them. Despite being in a deactivated state, they can still be a magnet for hackers. Additionally, find all plugins that have received no updates for a long time (from half a year to a year) and remove those too.
5. Make Backups of Your Site and Database and Make Them Often

This is probably the most important operation that will help you restore the normal functioning of your website if hackers have somehow managed to bypass all your safety precautions. That’s why we want to discuss the process of backing up your website files in detail.
HOW OFTEN TO BACKUP?
It depends on how frequently you update your content. If you add, edit, or remove your content very often, say every day, daily backups are what you surely need. While it may seem like overkill, you will be thankful that you’ve made enough copies when disaster strikes.
For websites whose content is refreshed comparatively seldom, biweekly or monthly backups will do.
WHERE TO KEEP COPIES?
One of the principal conditions for a backup to be successful is to keep copies in different places. Storing a backup in one location only is risky. Our recommendation is to save your files to three destinations:
- Your local machine (or an external storage device)
- The cloud
- The host
This way, you’ll definitely have at least one copy of your website left. Also, we recommend naming the folder with a backup inside by the date when you’ve made it.
HOW TO BACKUP
You can employ several methods to backup your website. All of them have their pros and cons. Here are three methods you can use. Try them all and decide which one works best for you.
Manual Backups
This method supposes manually copying your web and database files to your local machine via the FTP protocol using specialized file transfer tools like Filezilla.
The main benefit of this approach is that you can supervise the backup operation from the first to the last moment. The downside: it’s your responsibility to make backups on a regular basis and ascertain that all the assets have been transferred to the local computer.
Also, if your site has a lot of content, manual backups may take a long time. That said, if your site is based on WordPress (WP), you don’t have to back up all your web files. Just copy the wp-config.php file and the wp-content folder, which include everything that makes your site different from others (plugins, themes, and settings). The rest of the files make up the standard WordPress installation package. In addition, making a copy of the database is necessary.
Read the official WP guide for details.
Automated Backup Tools and Plugins
There are tons of automated backup solutions and plugins around. WordPress site owners can install one of the backup plugins they can find in the official WordPress Plugins directory.
Take the BackWPup plugin, for example. It completely automates the backup process, performing all the essential tasks for you, such as database backup, WordPress XML export, and generating a file with installed plugins. This tool also allows you to store your backups to various locations (FTP Server, S3 Services, Dropbox, and others).
Drupal users may find the All In One Backup useful. It provides the interface for exporting the project files and the database.
One downside of backup plugins is that you have to keep them up to date. As we said earlier, hackers always look for security holes in outdated plugins and modules.
You can also take advantage of various automated backup solutions like Dropmysite, Backupmachine, and Codeguard.
cPanel
Using cPanel is straightforward. Just follow the instructions. You should still remember to keep your files securely stored in several locations and name them appropriately.
WRAPPING UP
Keeping your website safe and sound requires a great deal of effort whatever technologies power it. We recommend implementing all the preventive measures we’ve described above.
You can contact us for any consultations regarding the security and performance optimization of websites based on the most popular content management platforms, including WordPress, Drupal, Magento, Joomla!, Shopify, Squarespace, and BigCommerce.









